Non-malignant Brain Tumour
What is it?
A brain tumour is a mass of abnormal cells in or around the brain. The cause of most brain tumours is unknown. Several factors may be associated with an increased risk of developing a brain tumour, including radiation exposure, a family history of brain tumours, and advancing age. Non-malignant brain tumours grow slowly and do not invade surrounding tissues. While non-malignant brain tumours are noncancerous (benign), their impact on brain function is nonetheless serious and may cause significant neurological symptoms, including behavioural and cognitive changes, dizziness, headaches, seizures, paralysis and even death. Although some tumours can be surgically removed, surgery is not always an option due to the location of the tumour in the brain. In many cases, radiation is used to treat non-malignant brain tumours.
Click to download the chart pack or infographic!
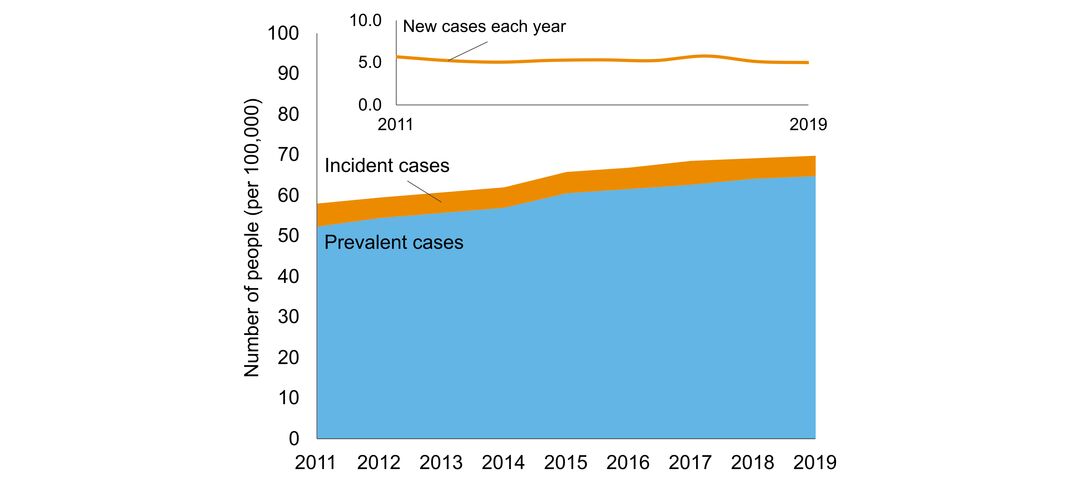
- number of people in Ontario with the disorder
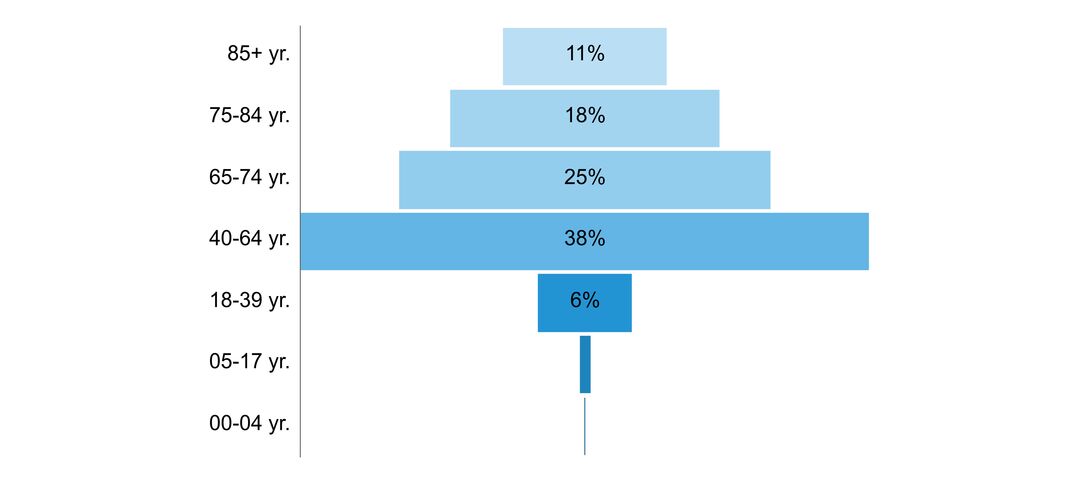
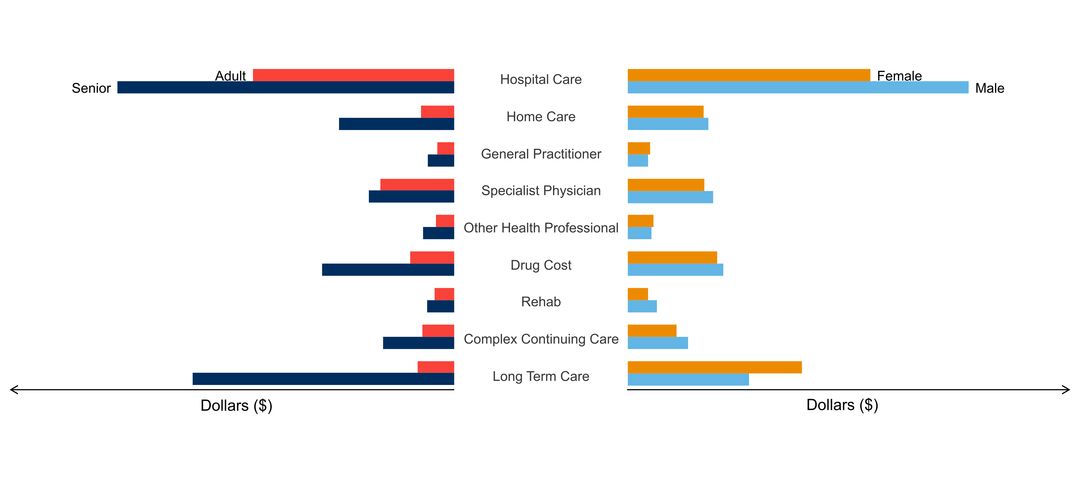
- age of people with the disorder
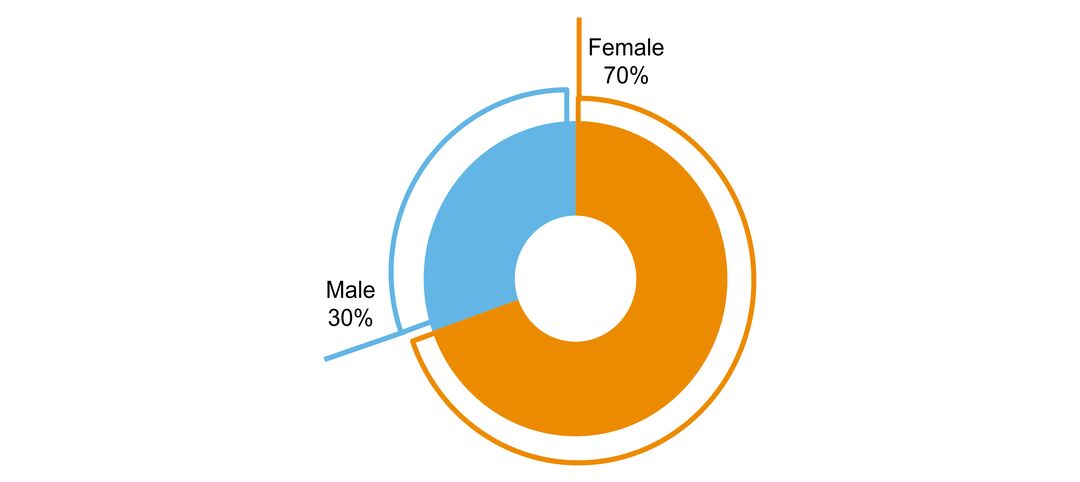
- sex ratio of people with the disorder
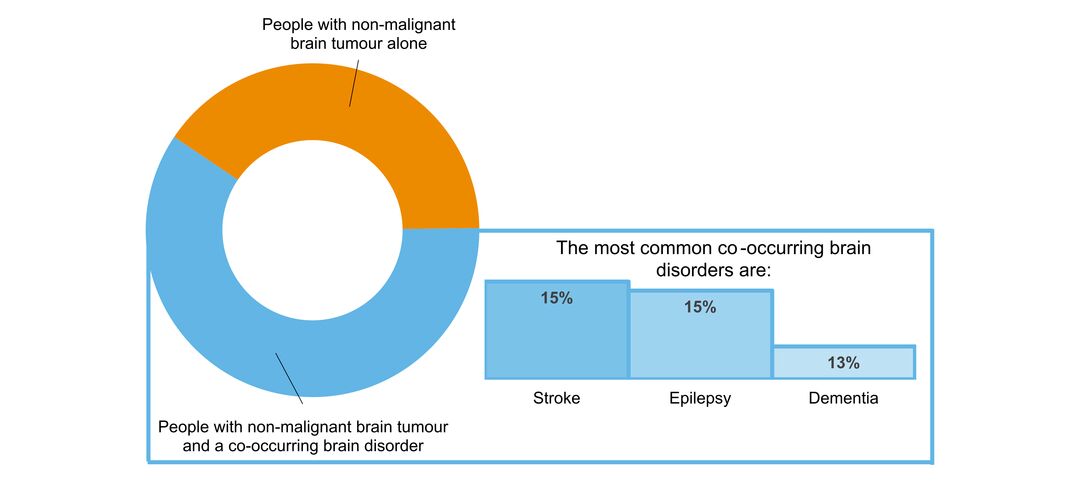
- what other brain disorders commonly co-occur
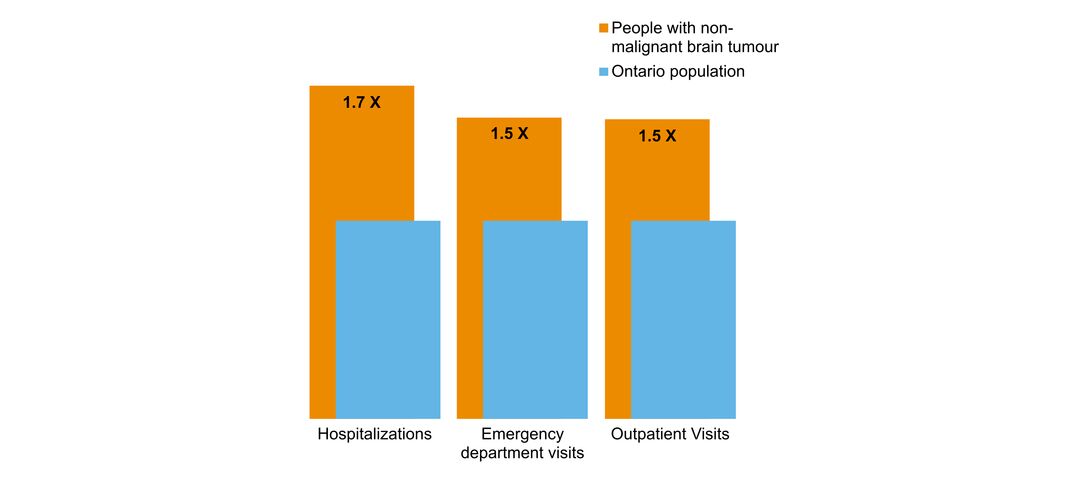
- overlap with mental health and addictions health system use
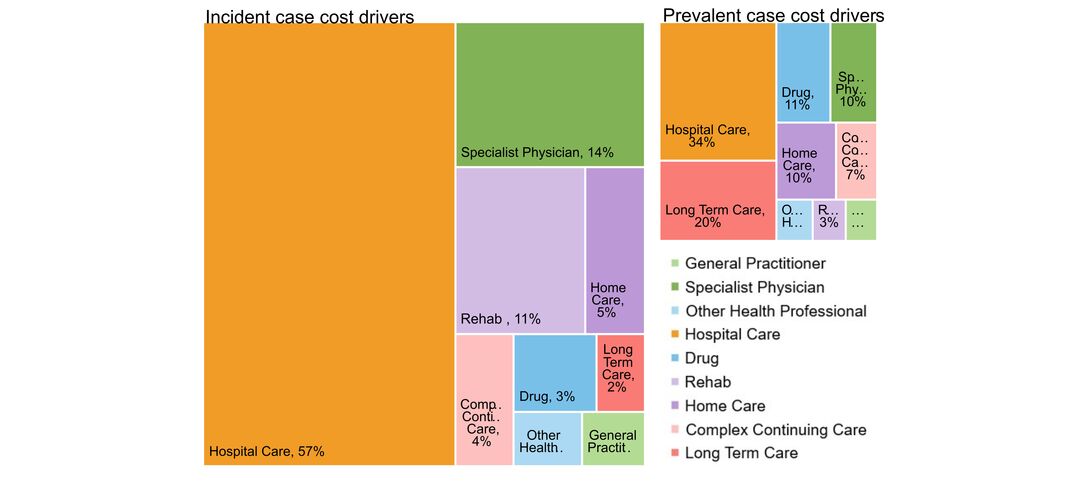
- costs & cost drivers associated with health system use